Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation and application of robots and computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing. These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans, in hazardous or manufacturing processes, or simply just resemble humans. Many of today’s robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics.
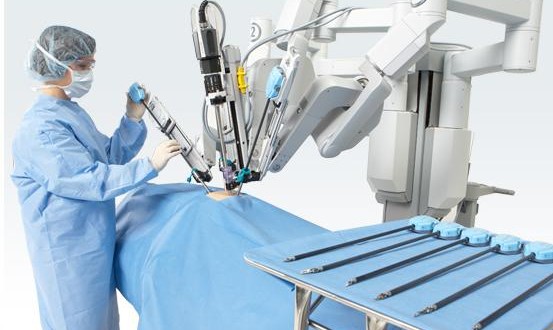
Robotic Surgery is the latest development in medical field. This surgery is performed with the help of electro-mechanically controlled hands. For complex problem related to Prostate, Kidney or Bladder, various types of surgical methods are available such as
- Open Surgery
- Laparoscopy Surgery
- Robotic Surgery
In case of complex problems, surgeries such as prostatectomy, nephrectomy or cystectomy requires dexterous approach, because the target is surrounded by complex nerves and organs which are tightly confined with the operating area.
In open surgery, surgeon has to make long scar to reach to the specific organ. This results in to heavy blood loss, leads to chances of infection and takes long time of recovery. Traditional laparoscopic surgery is also a good option to open surgery, but it limits the moments of surgeon’s hand. In case of complex surgery, there are chances that other organs get affected which leads to major complication.
Robotic Surgery is advanced version of laparoscopic Surgeries. If we take example of radical prostatectomy (Complete Removal of Prostate), then here the target (prostate) is delicate and tightly surrounded with the nerves affecting urinary control and sexual functions. Using the robots surgeon has a better control to spare surrounding nerves, which may enhance in recovery experience and clinical outcomes.
Robotic surgery may be used for a number of different procedures, including:
- Coronary artery bypass
- Cutting away cancer tissue from sensitive parts of the body such as blood vessels, nerves, or important body organs
- Gallbladder removal
- Hip replacement
- Hysterectomy
- Kidney removal
- Kidney transplant
- Mitral valve repair
- Pyeloplasty (surgery to correct ureteropelvic junction obstruction)
- Pyloroplasty
- Radical prostatectomy
- Tubal ligation
Robotic surgery cannot be used for some complex procedures.
Robotics in India
Currently, the robotic surgery in India is in its infancy. There are only 13 robots for a country having a population of over one billion. Of these, six were added in 2011. India is ideally suited for robotic surgery as the surgeons are skilled, the patient volume is high and a full spectrum of complex diseases is encountered. In India particularly, multi-speciality robotic surgery has a great future.
Dr Naresh Trehan at Escort hospital in 2001 procured the first robot in Asia and used it for cardiac surgery. The first urology robotic programme was started at AIIMS, New Delhi in 2006.
By far urology and gynecology segments perform most robotic surgeries. Especially in urology, the robot-assisted approach to prostate cancer surgery has become the number one method for removing cancer in the US.
In principle, robotic surgery replicates the steps of the open surgical operation. Experienced conventional surgeons can safely adopt this technology, provided they are committed to the technology and are willing to work for a smooth transition and receive training from established robotic surgeons. Professional urologic associations are currently creating guidelines that will provide a framework for training. However two important principles must be followed if robotic surgery is to be successfully practiced. First, care must be provided in the context of a close-knit surgical team. Second, there is no substitute for practice. These days’ surgeons can now improve their skills by using a robotic simulator, similar to the airline pilot using flight simulators to advance flight training.
 Urologist in Chennai | Robotic Urologist in India | Chennai Urology
Urologist in Chennai | Robotic Urologist in India | Chennai Urology